New Outpatient COVID-19 Treatments - Guidelines Knowledge Check
In January / February 2022, both the National Institutes of Health (NIH) and Infectious Diseases Society of America (IDSA) updated their COVID-19 recommendations to address the omicron variant and include two newly authorized oral antiviral treatments for ambulatory patients with COVID-19.
What do these guidelines state about the indications / contraindications of these two new oral drugs (molnupiravir and ritonavir/nirmatrelvir [plaxovid]) and the two previously authorized intravenous drugs (remdesivir and sotrovimab) that are now recommended for ambulatory patients with COVID-19 that is likely due to omicron?
Try this case and test your knowledge of the new guidelines for these outpatient COVID-19 treatments.
In a busy emergency department several patients are presenting with fever and mild to moderate COVID-19 symptoms (fatigue and various degrees of respiratory symptoms).
Four of these patients are testing positive for SARS-CoV-2 during a time when omicron is the dominant variant.
They all have various risk factors for severe COVID-19 disease and meet indications for COVID-19 treatment as an outpatient.
Question:
Which patient is correctly matched to an outpatient COVID-19 treatment option?
Answer Options:
Give the intravenous antiviral remdesivir to a 32-year-old diabetic patient who is pregnant in her second trimester and developed COVID-19 about 8 days ago.
Give the oral antiviral ritonavir/nirmatrelvir (plaxovid) to a 21-year-old single mother on birth control pills, who developed COVID-19 about 8 days ago.
Give the monoclonal antibody sotrovimab to a 13-year-old boy with sickle cell disease and estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) < 30 ml/min who developed COVID-19 about 8 days ago.
Give the oral antiviral molnupiravir to a 17-year-old overweight male (BMI 39%) who developed COVID-19 roughly 8 days ago. Upon questioning, he reveals that he recently married and now abstains from alcohol and instead drinks St. John's Wort tea in the evening to relax.
The correct answer is:
Give the monoclonal antibody sotrovimab to a 13-year-old boy with sickle cell disease and estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) < 30 ml/min who developed COVID-19 about 8 days ago.
Educational Objective:
List the indications and contraindications to the four currently authorized medications for treating the omicron variant in ambulatory patients with risk factors for severe disease.
Key Point:
The IDSA and NIH guidelines recommend the same 4 treatments for ambulatory patients with mild to moderate COVID-19 and risk factors for severe disease during times when omicron is the dominant variant.
The NIH guidelines also rank these options from highest to lowest preference:
- Paxlovid (nirmatrelvir 300 mg plus ritonavir 100 mg) orally twice daily for 5 days
- Sotrovimab 500 mg administered as a single intravenous (IV) infusion
- Remdesivir 200 mg IV on Day 1 followed by remdesivir 100 mg IV on Days 2 and 3
- Molnupiravir 800 mg orally twice daily for 5 days
Applying this ranking to real life is tricky because the top choice, paxlovid, has a very long list of contraindications and therefore is only the top choice for a surprisingly narrow group of patients. It might also come as a surprise that if paxlovid is contraindicated, the other 2 antivirals (remdesivir and molnupiravir) are NOT the next choices. Rather, the monoclonal antibody sotrovimab is the preferred second choice. Sotrovimab is the only remaining monoclonal antibody that is effective against omicron.
Helpful Table: A helpful table of all current (February 8, 2022) COVID-19 treatment options can be found at the following IDSA website (scroll down and click on “Overview of COVID-19 Treatment Guidelines (Summary Table)”. https://www.idsociety.org/COVID19guidelines
Explanation:
Adaptations of Outpatient COVID-19 Treatment Options to the Omicron Variant:
Prior to mid-December 2021, the three anti-SARS-CoV-2 monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) bamlanivimab plus etesevimab, casirivimab plus imdevimab, and sotrovimab were the only therapies recommended in the NIH Guidelines for nonhospitalized patients who presented with mild to moderate COVID-19 and were at high risk for progressing to severe disease.
When the Omicron variant became dominant (>80%) in many parts of the United States in December 2021/January 2022, 2 of these 3 available monoclonal antibody treatments (bamlanivimab plus etesevimab and casirivimab plus imdevimab) were rendered ineffective.
To counteract a predictable shortage of the only remaining anti-SARS-CoV-2 mAb treatment (sotrovimab), the NIH Panel added a 3-day course of intravenous (IV) remdesivir as a second outpatient treatment option. This was an off-label recommendation since remdesivir is formally only authorized for hospitalized patients. Soon after the addition of remdesivir to the outpatient options, emergency authorization was also granted for two new oral anti-Sars-CoV-2 agents (paxlovid and molnupiravir).
The NIH guidelines ranks these 4 omicron-effective choices as follows (from most to least preferred):
- Paxlovid (nirmatrelvir 300 mg plus ritonavir 100 mg) orally twice daily for 5 days
- Sotrovimab 500 mg administered as a single intravenous (IV) infusion
- Remdesivir 200 mg IV on Day 1, then remdesivir 100 mg IV on Days 2 and 3
- Molnupiravir 800 mg orally twice daily for 5 days
Choosing an Outpatient Omicron Treatment Option (apply this stepwise approach to the 4 above cases presented as answer options):
Step 1: Does my patient fall into a high-risk category?
The original FDA emergency use authorization for the anti-SARS-CoV-2 monoclonal antibodies defined high risk patients as follows (this includes their May 14, 2021 revision, when the FDA lowered the body mass index cutoff from ≥35 to >25 and removed age criteria that restricted use in patients with sickle cell disease, neurodevelopmental disorders, medical-related technological dependence, asthma, cardiovascular disease, hypertension, and chronic lung disease):
The FDA subdivides the risk of individual conditions as follows:
- AIIa refers to high-risk conditions well represented in clinical COVID-19 trials,
- BIII refers to medical conditions and factors with limited representation in clinical trials.
- AIII refers to a subgroup within the BIII group that is assigned a higher rating despite under-representation in COVID-19 trials, namely patients with immunocompromising conditions or receipt of immunosuppressive therapy:
-
- Aged ≥65 years (AIIa)
- Obesity (BMI >30) (AIIa)
- Diabetes (AIIa)
- Cardiovascular disease (including congenital heart disease) or hypertension (AIIa)
- Chronic lung diseases (e.g., chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, moderate-to-severe asthma, interstitial lung disease, cystic fibrosis, pulmonary hypertension) (AIIa)
- An immunocompromising condition or immunosuppressive treatment (AIII). Many experts strongly recommend therapy for patients with these conditions, despite their limited representation in clinical trials.
- Being overweight (BMI 25–30) as the sole risk factor (BIII)
- Chronic kidney disease (BIII)
- Pregnancy (BIII)
- Sickle cell disease (BIII)
- Neurodevelopmental disorders (e.g., cerebral palsy) or other conditions that confer medical complexity (e.g., genetic or metabolic syndromes and severe congenital anomalies) (BIII)
- Medical-related technological dependence (e.g., tracheostomy, gastrostomy, or positive pressure ventilation that is not related to COVID-19) (BIII)
- Infants aged <1 year (for bamlanivimab plus etesevimab only) (CIII)
Step 2: Does my patient have a contraindication (drug interaction risk) to Paxlovid?
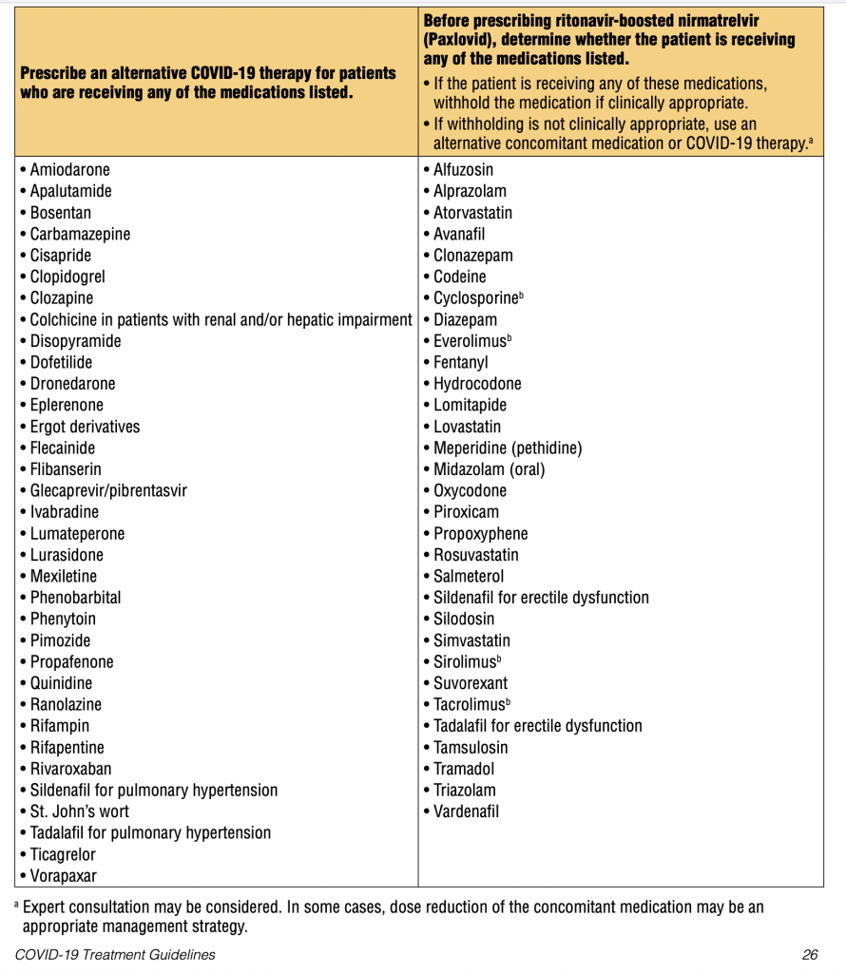
Paxlovid is (1) an oral pill that is (2) 88% effective in preventing severe disease, which are two factors that make it an attractive first choice for ambulatory care settings. However, paxlovid is a strong P450 inhibitor that interacts with a very long list of medications, including birth control pills (increased risk of unwanted pregnancy!), antihypertensives, statins, methadone, and also the herb St. John’s Wort (the use of which patients might not disclose because it is an herb). Since patients with COVID-19 risk factors tend to have multiple comorbidities and often take several medications, the risk of a (potentially life-threatening) drug interaction with paxlovid is significant (the guidelines recommend the consideration of a pharmacy consult). See "Figures and Downloads" below for lists of drugs provided by the IDSA and the NIH that may interact negatively with Paxlovid.
If this drug-interaction hurdle can be cleared, then most outpatients > 12 years-olds with mild to moderate COVID-19 and risk factors for severe disease can be treated with Paxlovid. The other precautions with paxlovid are as follows: paxlovid should not be given to patients with severe liver or renal disease (eGFR<30 L/min). For pregnant patients, paxlovid might increase maternal complications (such as pre-eclampsia). There are insufficient data to judge fetal risk.
Paxlovid must be started within 5 days of symptom onset.
Step 3: If paxlovid is not an option, can my patient receive sotrovimab?
The biggest problem with sotrvimab is shortage of the drug. Otherwise, it performs very well in the outpatient setting since it is (1) a single IV dose and (2) 85% effective at preventing severe COVID-19. It can be administered to patients > 12 years old and has no known contraindications. There are no known adverse pregnancy effects, and neither renal nor hepatic disease is a contraindication. There are also no known drug interactions.
Sotrovimab has the longest window of effectiveness after symptom onset: it can be started within 10 days of the first symptoms.
Step 4: If sotrovimab is not an option, can my patient receive remdesivir?
Remdesivir qualifies as the somewhat lower #3 choice only because it is a 3-day IV infusion course, which creates logistical problems in an ambulatory setting. Otherwise, remdesivir performs very well: it is 87% effective at preventing severe COVID-19, can be administered to patients > 12 years old and is only contraindicated (aside from allergy to the medication) in patients with severe renal disease with eGFR <30 mL/min (a dose adjustment is recommended for those with eGFR >30 mL/min and <60 mL/min). There are no known adverse pregnancy effects or known drug interactions.
Remdesivir must be started within 7 days of symptom onset.
Step 5: If remdesivir is not an option, can my patient receive molnupiravir?
Molnupiravir is a pill, which makes it convenient; however, it carries a warning that it should only be considered when the other 3 treatments are not available since it is not very effective (30% effective) and carries genetic risks (may alter the patient’s DNA). Molnupiravir can only be given to patients > 18 years-old because it negatively affects bone and cartilage growth. Molnupiravir is contraindicated in pregnancy. Since molnupiravir may be mutagenic, both males and females should also abstain from initiating a pregnancy while either partner is taking molnupiravir. Due to the low effectiveness and the potential for genetic effects, the guidelines state that it is reasonable for patients with lower risk comorbidities to discuss risk/benefit considerations before deciding to take molnupiravir. No dose adjustment is required in patients with any degree of renal or hepatic disease.
Just like paxlovid, molnupiravir must be started within 5 days of symptom onset.
_______________________________________________
These 4 treatment options can also be conceptualized from the following perspective:
Effectiveness: paxlovid – 88%; Sotrvimab 85%; remdesivir 87%, Monupliravir 30%
Age: Patients must be 18 years or older for molnupiravir. Patients 12 years and older qualify for the other 3 drugs.
Treatment Window after Symptom Onset: the two pills - paxlovid and molnupiravir - must be taken within 5 days of symptom onset. The 3-day IV course of remdesivir can be started for up to 7 days, and the single IV dose of sotrovimab for up to 10 days after symptom onset.
Comorbidity Risk Factors: comorbidities (including sickle cell disease) per se are indications, not contraindications to these 4 medications. The only problem posed by comorbidities is the fact that these patients often already take multiple medications, which may mostly interact negatively with paxlovid.
Drug Interactions: only paxlovid – a P450 inhibitor – is known to have significant (and potentially life-threatening) drug interactions. A fact that may be easily missed unless the patient is specifically asked about it: in patients using oral contraceptives, paxlovid might increase the risk of unwanted pregnancy. In patients taking the herb St. John’s Wort, paxlovid might not be effective. Follow these links to lists of drugs provided by the IDSA and the NIH that may interact negatively with paxlovid. See "Figures and Downloads" below for lists of drugs provided by the IDSA and the NIH that may interact negatively with Paxlovid.
Pregnancy: overall, pregnancy data are lacking, so safety in pregnancy cannot truly be stated for any of the 4 options. No adverse pregnancy effects have been reported for sotrovimab or remdesivir; paxlovid may increase maternal complications (pre-eclampsia, etc), and molnupiravir is contraindicated in pregnancy. Partners should be advised to also not initiate a pregnancy while either partner is taking mulnupiravir.
Hepatic/Renal Disease: sotrvimab and molnpiravir do not require any adjustment for hepatic or renal disease. Remdesivir requires dose adjustment for eGFR >30 and <60 mL/min. Neither remdesivir nor paxlovid are recommended for patients with eGFR <30 mL/min. In addition, paxlovid is not recommended in patients with severe hepatic disease.
Genetic Effects: only molnupiravir has a risk of altering the patient’s own DNA.
Helpful Table: a helpful table of all current (February 8, 2022) COVID-19 treatment options can be found at the following IDSA website (scroll down and click on “Overview of COVID-19 Treatment Guidelines (Summary Table)”. https://www.idsociety.org/COVID19guidelines
Figures and Downloads
Figure 1: IDSA.org Paxlovid Drug Interaction List
Figure 2: NIH Paxlovid Drug Interaction List
References:
The National Institutes of Health COVID-19 Treatment Guidelines: https://www.covid19treatmentguidelines.nih.gov/critical-care/ (Updated January 19, 2022) (Accessed February 14, 2022). https://files.covid19treatmentguidelines.nih.gov/guidelines/archive/covid19treatmentguidelines-01-19-2022.pdf
Infectious Diseases Society of America Guidelines on the Treatment and Management of Patients with COVID-19. https://www.idsociety.org/COVID19guidelines (Updated February 8, 2022) (Accessed February 14, 2022)
Gottlieb RL, Vaca CE, Paredes R, et al. Early remdesivir to prevent progression to severe COVID-19 in outpatients. N Engl J Med. 2021. Available at: https://www.nejm.org/doi/full/10.1056/NEJMoa2116846.
Fact sheet for healthcare providers: emergency use authorization for molnupiravir. https://www.fda.gov/media/155054/download (Accessed February 14, 2022).
Dr. Andrea Eberly is one of the seasoned medical experts that contribute to Med-Challenger Medical Education products for medical board certification exam preparation, maintenance of medical certification, and continuing medical education requirements.
About Med-Challenger:
Med-Challenger provides online medical education exam review and continuing medical education products and services to physicians, nurses, and other medical specialists as well as learning management systems for medical training programs and healthcare groups world-wide via its web-based medical education library and world-class assessment platform at https://app.challengercme.com.